 24 Dec,2025
24 Dec,2025
Which types of built-in shutter aluminum profile are best for sound insulation?
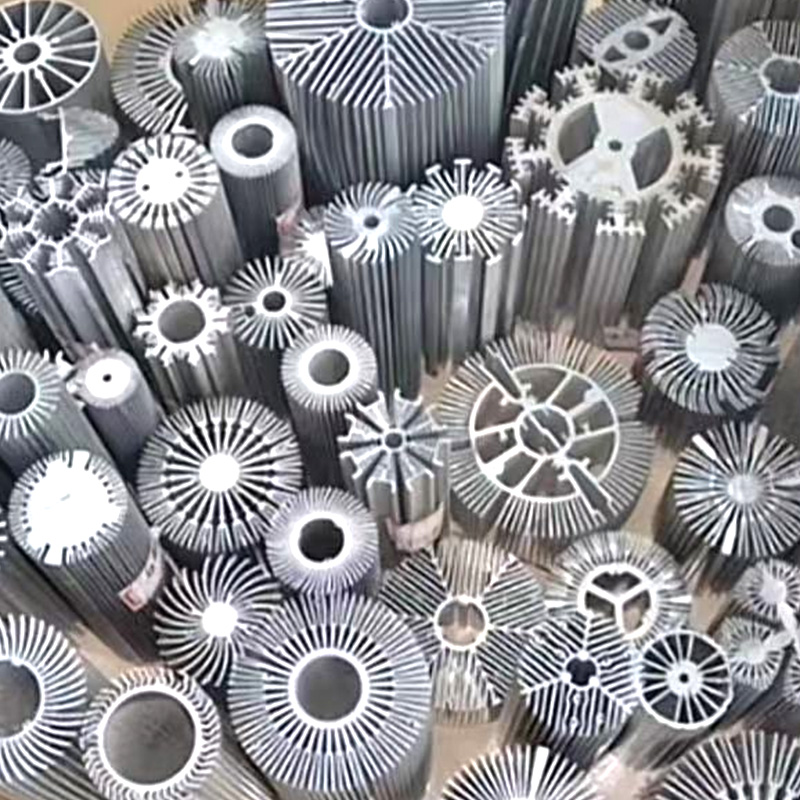



The sunflower radiator adopts advanced heat pipe direct contact and multi-fin cooling technology. The sunflower radiator can quickly and evenly disperse and efficiently discharge the heat generated by high heat sources such as CPU and graphics card, ensuring that your computer remains cool under high-intensity operation, extending the service life of the hardware and improving the overall system stability. Its unique sunflower petal-shaped fin design not only increases the heat dissipation area but also optimizes the airflow path, making the heat dissipation effect more excellent. In terms of appearance design, the sunflower radiator abandons the monotony and bulkiness of traditional radiators and shows the fusion of technology and aesthetics with streamlined contours and exquisite craftsmanship. It is made of high-quality environmentally friendly materials to reduce the impact on the environment. At the same time, the efficient heat dissipation performance helps to reduce the increased energy consumption of the computer due to overheating and achieve a green and energy-saving experience.
Years Industry Experience
Factory Area
Current Staff
Annual Output
 24 Dec,2025
24 Dec,2025
 18 Dec,2025
18 Dec,2025
 11 Dec,2025
11 Dec,2025
 04 Dec,2025
04 Dec,2025
 24 Nov,2025
24 Nov,2025
 20 Nov,2025
20 Nov,2025
Sunflower radiators are an efficient heat dissipation solution that is widely used in a variety of equipment and systems, especially in the industrial and commercial fields. Here are some of the main application scenarios:
Mechanical equipment: In many industrial machinery, Sunflower radiators can be used to dissipate heat, such as engines, compressors, and pumps, to keep the equipment at a suitable operating temperature.
Power equipment: In power plants and substations, Sunflower radiators are used to cool transformers and generators to improve efficiency and extend the life of equipment.
Air conditioning systems: Sunflower radiators can be used in large commercial air conditioning systems to help dissipate heat and ensure stable operation of the system.
Automotive industry: In the automotive manufacturing process, Sunflower radiators can be applied to cooling systems to help control engine temperature and prevent overheating.
Refrigeration equipment: In the refrigeration and cold storage industry, Sunflower radiators are used in compressors and condensers to improve cooling efficiency.
Electronic equipment: In data centers and computer servers, Sunflower radiators can effectively cool high-performance computer components to prevent overheating.
Chemical Industry: During the chemical production process, sunflower radiators can be used to control the temperature in reactors and pipelines to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the reaction.
Food Processing: In the food processing industry, sunflower radiators can be used to cool equipment to ensure that food remains safe and sanitary during the production process.
HVAC Systems: In the heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems of buildings, sunflower radiators are used to improve the heat exchange efficiency of the overall system.
Agricultural Equipment: In agricultural machinery, sunflower radiators can be used to dissipate heat, such as in equipment such as tractors and harvesters, to ensure that the equipment operates normally when under high load.
What are the key technical parameters to consider when selecting a Sunflower radiator, such as heat dissipation capacity and size?
There are several key technical parameters to consider when selecting a Sunflower radiator to ensure its performance and efficiency in a specific application. Here are some important technical parameters:
Cooling Capacity: The cooling capacity of a radiator is usually expressed in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). When selecting, it is necessary to ensure that the radiator can effectively remove the generated heat based on the heat load requirements of the equipment.
Dimensions: The dimensions of a heat sink (length, width, and height) affect the space in which it will be installed and how well it will cool. Make sure the heat sink you choose can accommodate the space constraints of the installation environment.
Material: The material of the heat sink affects its durability, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Common materials include aluminum, copper, and steel. It is important to choose the right material for the specific operating environment.
Fan Type: Many heat sinks have fans to enhance cooling. Consider the fan type (e.g., centrifugal or axial), air volume, and noise level.
Fluid Type: If the heat sink is used in a liquid cooling system, make sure the coolant (e.g., water, glycol, etc.) is compatible with the heat sink material.
Operating Pressure: The heat sink should be designed to withstand the operating pressure in the system. Confirm that the maximum operating pressure of the selected heat sink meets the application requirements.
Heat Exchange Area: The larger the heat exchange area of the heat sink, the better the heat dissipation is generally. Make sure the selected heat sink has enough heat exchange area to meet the heat load requirements.
Installation Method: Understand the installation method (e.g. vertical, horizontal) and required accessories of the radiator to ensure compatibility with the equipment.
Environmental Compatibility: The performance of the radiator under specific environmental conditions, such as the ability to work in high temperature, high humidity or corrosive environments, must be evaluated.
Maintenance Requirements: Understand the maintenance requirements of the radiator, including the frequency of cleaning and replacement of parts, to ensure its long-term reliability and efficiency.